PANTSIR-S1 AIR-DEFENCE MISSILE GUN SYSTEMAuthor: Igor Stepanichev, Valery Slugin - Igor Stepanichev, acting director general of KBP Instrument Design BureauValery Slugin, general designer of discipline, section chiefMilitary Parade, No. 6, 2011, page(s): 6-11
The Pantsir-S1 air- defence missile gun system (ADMGS) is the natural evolution of the Tunguska system designed in Tula by KBP instrument Design Bureau and put into service in 1982. The performance capabilities of air attack platforms changed drastically since the Tunguska system was put into service with the Soviet Armed Forces. There have emerged small size unmanned aerial vehicles, low altitude high precision cruise missiles and remotely guided combat and reconnaissance aerial vehicles featuring extremely low optical, radar and IR signature. Flight speed of some targets increased up to 1000 m/s. Missile armament of the Tunguska ADMGS intended for engagement of large manned aircraft turned out to be ineffective when countering new threats.
The Pantsir-S1 ADMGS was developed to fundamentally change the system's performance capabilities in terms of interception zones, reduction of time required for operation, capability to engage all types of targets and broader use of missile armament.
Outcome of the modern military conflicts (Yugoslavia, Afghanistan and Iraq) was to great extent determined by concentrated air strikes effected against the most important military and economic assets into the depth of the countries' territory.
Analysis of the said conflicts revealed that all air raids commence with suppression of the enemy's air defence by concentrated air attacks with the use of precision-guided weapons like Harm (ARM), cruise missiles like Tomahawk and guided aircraft bombs like GBU-15 and GBU-16.
A large number of drones may be flying above the objects under attack for adjustment of target coordinates and assessment of air raid efficiency
The system features:• multitarget capability, i.e. engagement of virtually all types of aerial targets, primarily all types of precision-guided munitions approaching an object under defence at a speed of up to 1000 m/s from different directions, aircraft flying at a speed of up to 500 m/s, helicopters, UAV, as well as lightly armoured ground targets and enemy's manpower;
• combined missile and gun armament ensuring continuous impact area and continuous firing starting from a distance of 18-20 km to 200 m from targets at altitudes of 10 m to 15 km;
• multimode adaptive radar and optical weapon control system operating in UHF, EHF and IR wavebands, this ensuring high jamming immunity and survivability under electronic countermeasures and suppression by fire with the use of ECM means and HARM missiles, and high reliability of the system operation;
• high target engagement rate due to short reaction time, high speed missiles and availability of multi channel control system operating in wide sector;
• the use of high precision command missile guidance system allowed development of a small size and high maneuverability surface-to-air missile (SAM) featuring high efficiency and low cost;
• large number of missiles in one combat vehicle (12 pcs.);
• small size two-stage bi-caliber SAM with solid fuel booster ensuring high average speed, maneuverability and efficient engagement of all types of targets due to high lethality fragmentation rod warhead and high precision SAM guidance system;
• firing against a receding target ensures double increase of impact depth and the systems performance capabilities when used against manned aircraft, UAV, strategic cruise missiles and tactical cruise missiles;
• firing missiles on the move extends the system's combat application;
• fully automatic combat operation mode both as a stand-alone unit and within a battery consisting of several combat vehicles, this allowing to reduce psychophysical stress to crew members;
• independent combat use due to availability of means of detection, tracking and engagement in one combat vehicle;
• modular design of combat vehicle and system as a whole allows various modifications based on the basic system.
during an air attack. Moreover, sabotage groups airdropped in soft-skinned and lightly-armoured vehicles may break through to important objects under defence.
Therefore, SHORAD systems are also intended to engage drones, light combat vehicles and enemy's manpower in area of the defended objects.
Large number of targets and high density of air attacks require air defence assets to ensure high target engagement rate, as well as to possess a numerous ready-to-fire and quickly replenishable ammunition load.
Because of their high price the long range air-defence systems may not be available in sufficient quantity to ensure direct defence of a large number of small size and pin-point military and economic objects with a radius of 1.5-3.0 km which amount to minim of 70% of all the objects to be defended. Besides, the long range air-defence systems can not make use of their capabilities in short range and when used against low altitude targets in difficult terrain.
SHORAD systems with maximum firing range of 15-20 km play an important part in air defence. Systems of this class significantly outperform the long range systems in terms of cost efficiency.
The Pantsir-S1 SHORAD system (see the photo of the combat vehicle in Fig.1) designed at KBP Instrument Design Bureau (KBP) is intended for air defence of important small size and pin-point military and industrial objects, infantry units and tactical formations as well as for reinforcement of air defence groups at low and extremely low altitudes when countering concentrated air strikes effected with the use of precision-guided weapons.
Table 1 describes the main performance specifications of the Pantsir-S1 combat vehicle.
The mobile version of the Pantsir-S1 system includes: combat vehicles (up to 6 CV in one battery), surface-to-air missiles, 30mm rounds, transporter-loader vehicles (one loader per two CV), maintenance equipment and training equipment.
The combat vehicle is intended to perform the tasks assigned to the system in terms of engagement of a wide range of aerodynamic and ground targets including those lightly armoured and enemy's manpower.
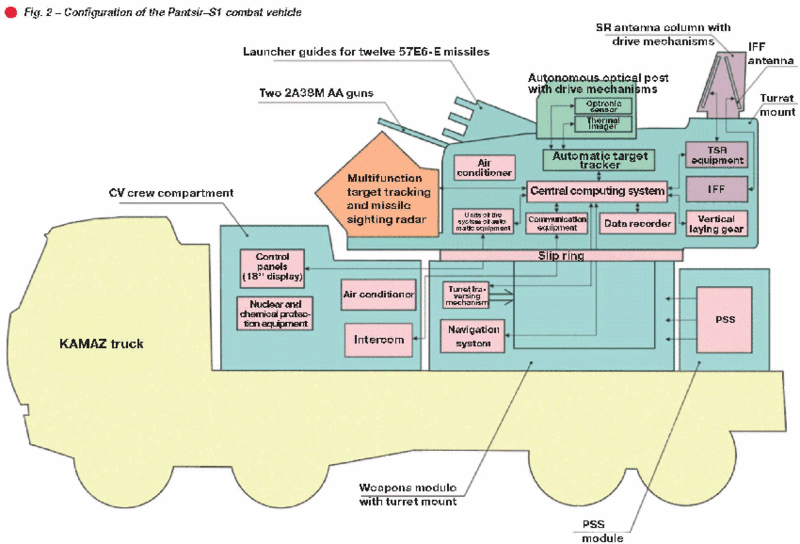
Configuration of the system CV is described in Fig.2.As seen in the figure the CV features modular design:
• control module accommodating CV crew;
• weapons module;
• turret mount;
• power supply system compartment (PSS).
The modular design allows various system configurations including stationary variant.
Various configurations of Pantsir-S1 AD system are shown in Fig. 3.
The system may be mounted on lightly armoured vehicles providing powerful and mobile air-defense asset for airborne assault troops, as well as on wheeled and tracked chassis for Air/Land Forces air-defense units or Navy vessels.
The information assets of the air-defense system include target search radar (TSR), target/missile tracking radar (TTR) and optical/electronic system (OES).
Make-up of the TSR is shown in Fig. 4.TSR provides automatic tracking of up to 20 targets, submitting three coordinates and radial velocity component for each target into CV central computer. Besides that TSR identifies friendly/enemy targets and target types (plane, helicopter, small-size target), thus increasing the system kill probability.
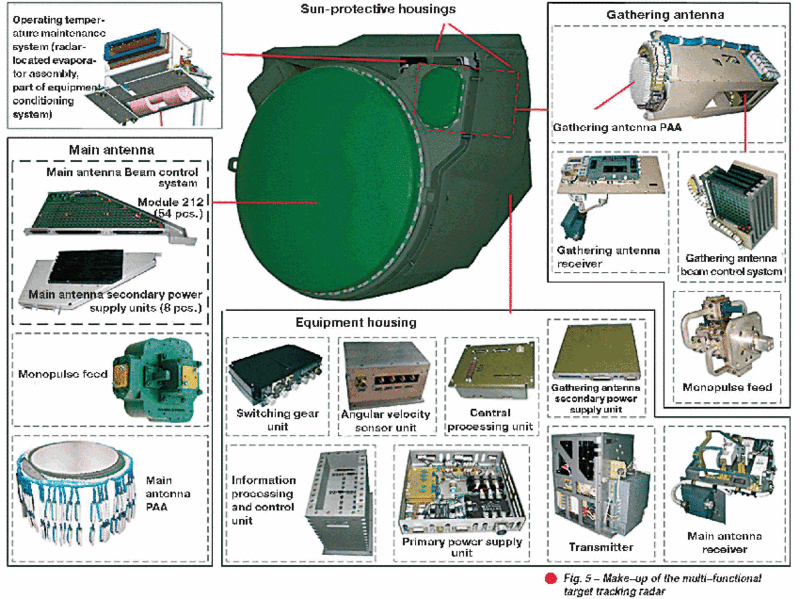
High combat performance of Pantsir-S1 AD system is guaranteed substantially due to employment of multi-functional target tracking radar (TTR) featuring phased antenna array (PAA). The make-up of the TTR is shown in Fig. 5.
The TTR incorporates two stations one of which is a receive-only terminal intended for SAM beacon signal perception by few-element phased antenna array (PAA), the latter measuring three coordinates of SAM and employed for missile gathering into main radar pattern. The second multi-element PAA station is a transmitting-receiving antenna irradiating both SAM and target with the following specifications:
• coordinates determination accuracy:
- in azimuth, mrad - 0.2
- in elevation, mrad - 0.2
- in range, m - 3.0
- in velocity, m/sec - 2.0
• simultaneous automatic tracking:
- targets - up to 3
- missiles - up to 4
- maximum target detection range, RCS 2 m2, km - 24
- operating band - K
Table 1 - The main performance specifications of the systemSpecification
Value
Armament
Missile and gun
Ammunition load, pcs:
• SAM in launcher guides
12
• artillery rounds
1400
Control system configuration
Target search radar, target tracking radar with phased antenna array, autonomous optical electronic system
Number of targets fired at simultaneously within the sector of ± 45°, pcs
4
Airplane detection range, km
32 - 36
Airplane tracking range, km
24 - 28
Impact zones, m:
by missiles
• in range
1200 - 20000
• in altitude
10 - 15000
by guns
• in range
200 - 4000
• in altitude
0 - 3000
Maximum speed of targets, m/s
1000
SAM guidance system
radio command with IR and radar sighting
Response time, s
4 - 6
Missile salvo capability
ensured
Day and night, all-weather operation of gun and missile armament
ensured
Engagement of ground targets by guns and missiles
ensured
Firing guns and missiles on the move
ensured
Crew members
3
Employment of PAA allows for implementation of three firing channels for three targets in all-weather radar mode, thus, the most critical target may be engaged with 2 SAM salvo. Besides, by means of the PAA gathering, the TTR provides radar acquisition and SAM gathering from the dispersion area of the first unguided stage of the missile flight into precise guidance channel of the main PAA. Employment of radar gathering allows for significant improvement of the missile flight performance due to application of high-energy composite propellant booster.
Along with target angular coordinates and range tracking the TTR also measures three coordinates of the SAM (two angles and range) based of the SAM beacon signals and transmits guidance commands to SAM.
The TTR operates in HF wave band providing for high precision of angular coordinates measurement and low-altitude targets handling.
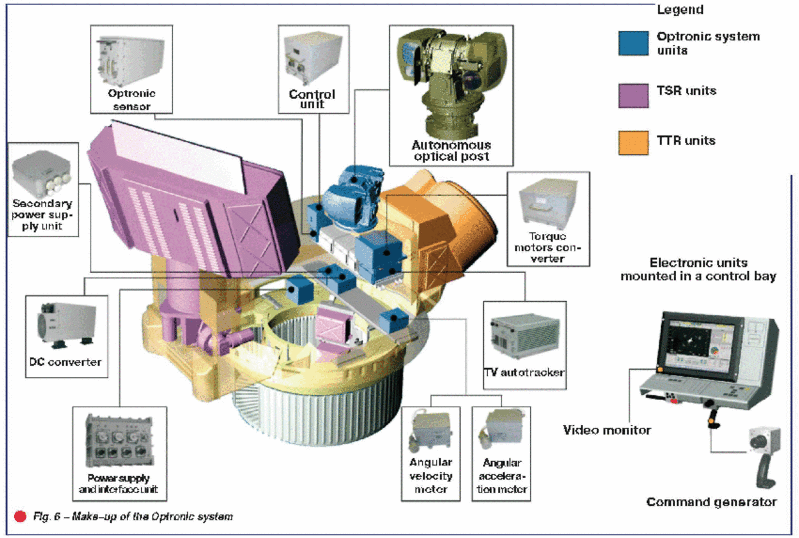
Firing against ground targets and extremely low-altitude targets employs optical\electronic system (OES) of target and missile tracking. The make-up of the OES is shown in Fig. 6.
The OES is integrated into autonomous optical post (AOP) intended for laying the OES optical axes according to the signals received from the central computer within the following angular range:
CV main features:• independent combat operation;
• combined missile and gun armament;
• multimode jamming resistant radar optical guidance system;
• all-weather capability;
• automatic combat operation mode;
• simultaneous firing against four targets;
• coordination of actions within the battery;
• armour protection of the crew against bullets and splinters.

• in azimuth, degr. - ± 90
• in elevation, degr. - from - 5 to + 82 OES provides final targeting
according to the target designation received from CC and automatic target acquisition as well. Target tracking is conducted in 3 -5 ƒm IR range and provides round-the-clock application of missile armament in optical operation mode. Automatic tracking range (with weather visibility range of 10 km) is as follows:
• F-16 aircraft, km - 17.0 - 26.0
• ARM "Harm", km - 13.0 - 15.0
• CM ALCM, km - 11.0 - 14.0
SAM sighting is conducted in close IR range spectrum (0,8 µm), the missile sustainer stage is sighted by the SAM optical responder pulse signals providing high jamming immunity of the channel from thermal dummy targets.
Narrow fields of view of the optical channels and high accuracy of the AOP gearless engine drives ensure measuring of the target and missile angular coordinates no worse than 0.05 mrad in azimuth and elevation channels.
Systematic errors of the missile and target channels of the OES are eliminated during the SAM launch while the process of automatic cross adjustment of the missile and target localizers is running.
Accurate measurement of the missile angular deviations from the target line-of-sight ensures high-precision missile guidance at a target in the optical mode of the control system. Optical mode provides missile firing against targets flying at extremely low altitudes (at a 5m altitude above water surface) and against ground targets.
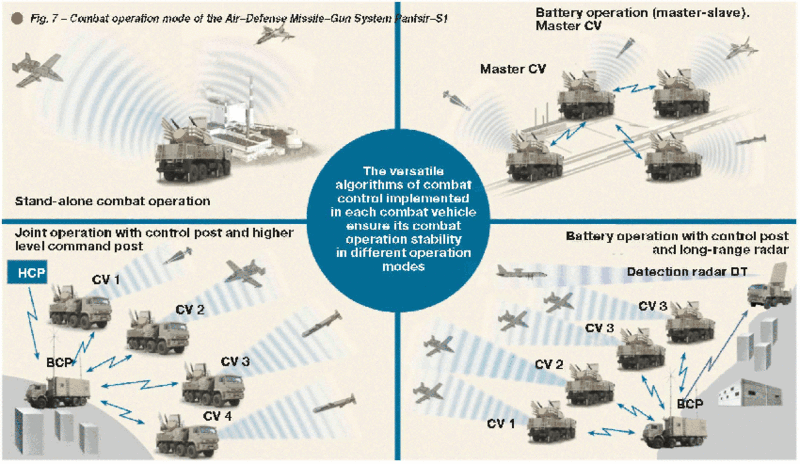
This combat vehicle equipment makes its stand-alone operation possible. Availability of the hardware with digital communication channels enables Pantsir-S1 system to conduct battery operation in different modes:
• stand-alone combat operation;
• joint operation with command post;
• battery operation in master-slave mode;
• battery operation jointly with command post and long-range radar.
Different modes of Pantsir-S1 operation are shown in the Fig.7Main features of the control system:
• simultaneous firing against four targets flying in the ±45° sector owing to the use of the multifunctional tracking radar incorporating the EHF-band phased antenna array and independent optical channel;
• high immunity to any type of jamming owing to integration of the radar and optical-electronic means into the single system which is able to function in dm-, mm-, and IR wave bands;
• capability of salvo firing by two missiles against one target owing to the use of the target tracking radar (TTR);
• short reaction time within 4 - 6 sec. owing to the automatic tracking of up to
The Pantsir-S1 ADMGS was developed to fundamentally change the system's performance capabilities in terms of interception zones, reduction of time required for operation, capability to engage all types of targets and broader use of missile armament.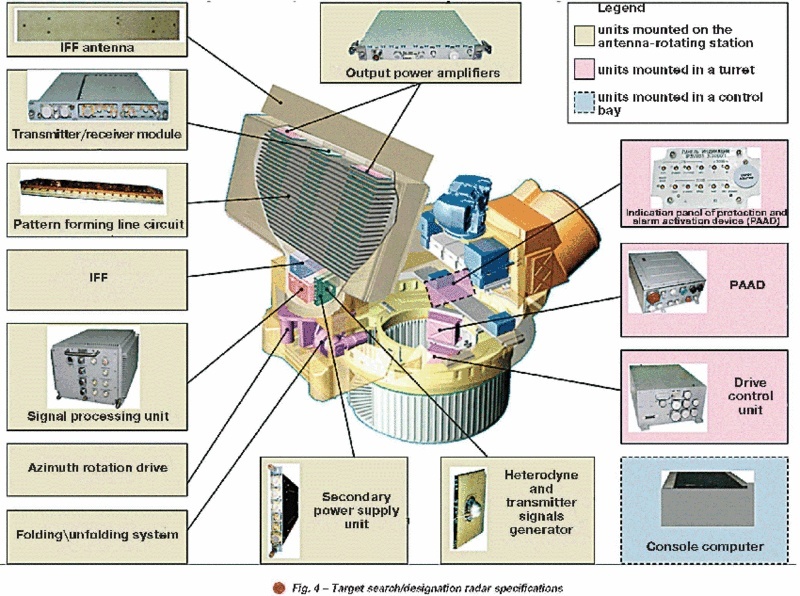
20 targets by the target search radar (TSR) and target designating with an accuracy ensuring fast final targeting and target acquisition by TTR and optical-electronic system (OES);
• computation of informative characteristics including target motion rate and target characteristics, selection of weapon type and assigning firing mode;
• realization of a complete combat operation cycle - from targets searching to their destruction in automatic mode;
• crew combat operation semiautomatic mode capability.
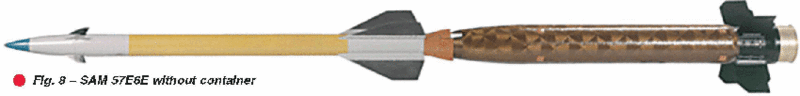
The two-stage air-defense guided missile 57E6-E (Fig.

features.
The gun armament consists of two 2A38M double-barrel AA automatic guns adopted from the Tunguska-M1 weapon system. They are capable to engage air and ground-based targets in a zone of up to 4 km in range and of up to 3 km in altitude.
High performance characteristics of the air-defense missile-gun system Pantsir-S1 ensure great advantage over foreign countries short-range AD systems for the AD systems supplied with Pantsir-S1.
 Purpose:
Purpose:• target designation reception, fine search, automatic target acquisition and tracking:
- trajectory tracking- up to 8
- priority targets - up to 3
• post-launch automatic acquisition and tracking of up to 4 SAM
• encoding and transmission of guidance commands to the tracked SAMs
Features:• main transmitting\receiving antenna with multielement feed-through mm-band PAA ensuring high-precision target and SAM tracking
• gathering phased-array receive-only antenna ensuring acquisition and gathering of SAM into main array
Azimuth coverage zone, degr...........................................±45
(360° subject to turret rotation)
Elevation coverage, degr...........................................-5 to +85
Maximum target tracking range, km:
- RCS=2m2 .........................................................24
- RCS=0.03m2........................................................7
Fine search area following TSR target designation
in 1 sec. with 0.9 probability:
- In azimuth, degr...................................................±2.5
- In elevation, degr..................................................±2.5
- In range, m......................................................±200
Target coordinates measurement precision:
- azimuth/elevation, mrad............................................0.2/0.2
- range, m .........................................................3.0
- velocity, m/sec......................................................2
Radial velocity measurement range, m/sec
-target......................................................10 to 1000
-SAM ......................................................30 to 2100
Simultaneous tracking:
- targets........................................................up to 3
- SAMs ........................................................up to 4
Operating band.......................................................K
Characteristic features:
- short flight time on the launch trajectory (t - 2.4s, Vmax = 1300m/s);
- high maneuverability after booster separation;
- low ballistic deceleration during booster-free flight (decrease of speed of 40 m/s over 1km);
- extended engagement envelope of 20km in range and 15 km in altitude;
- heavy weight of the warhead (20kg) at missile's low launch weight (75.7 kg)