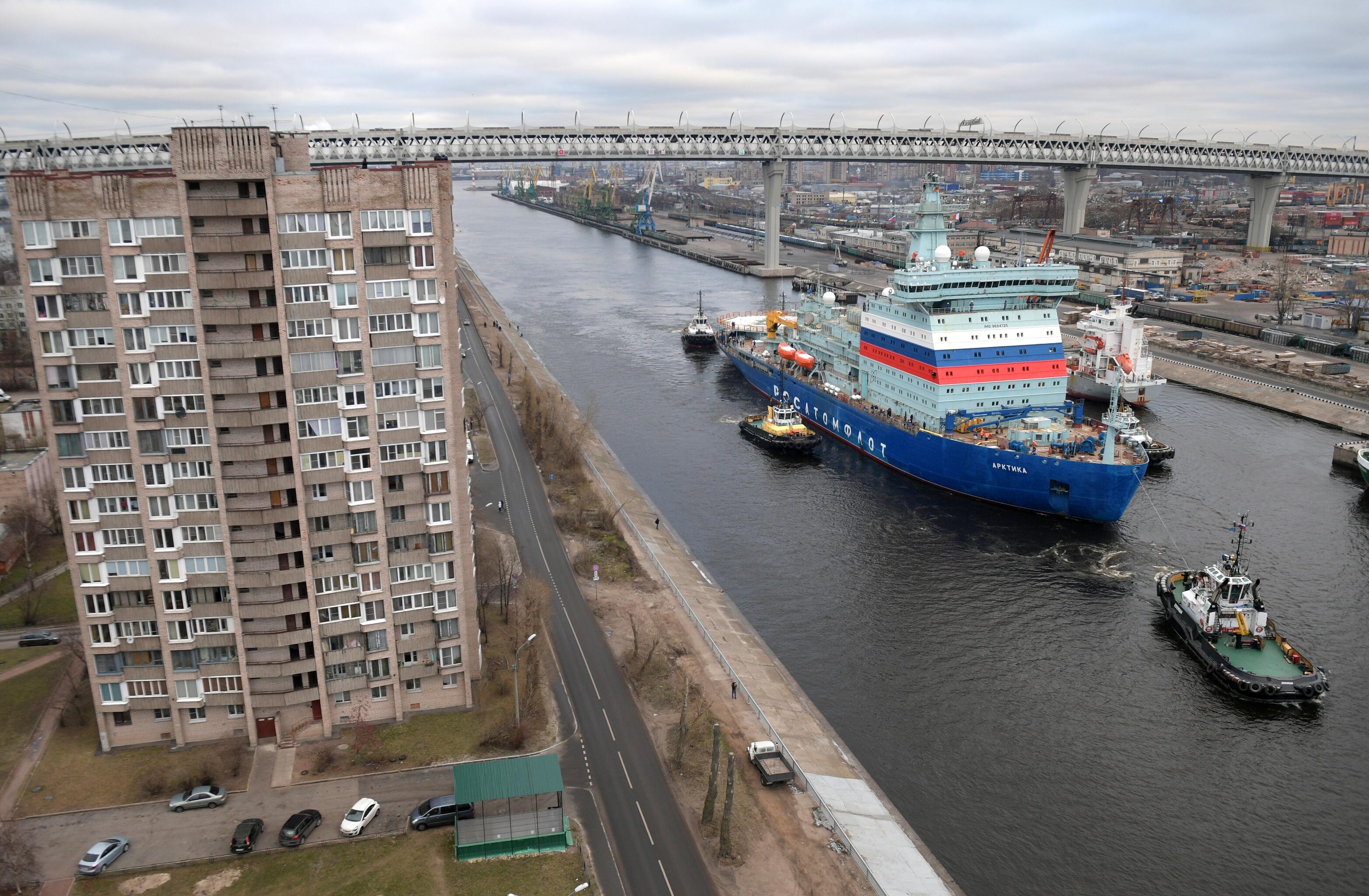
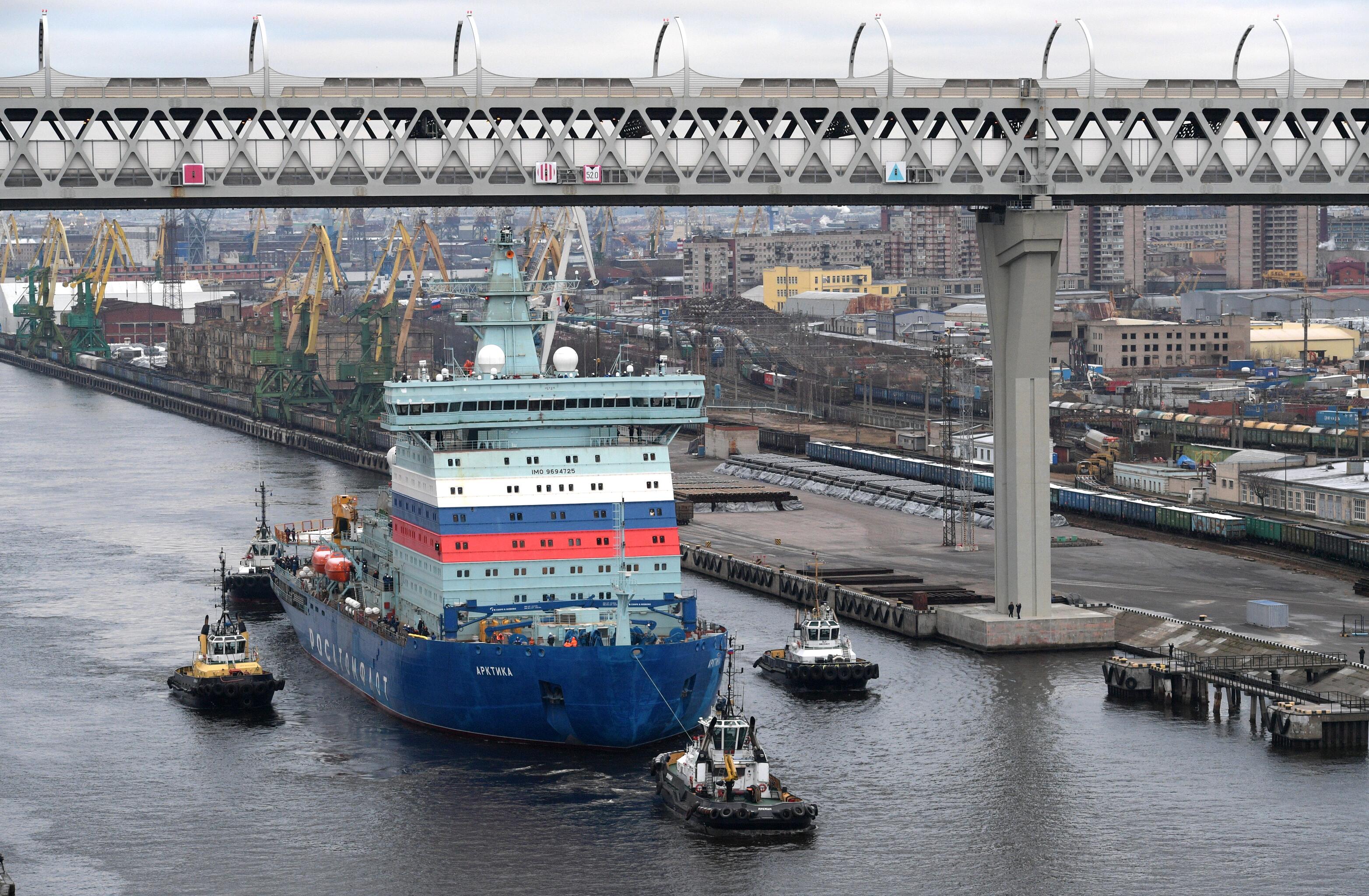
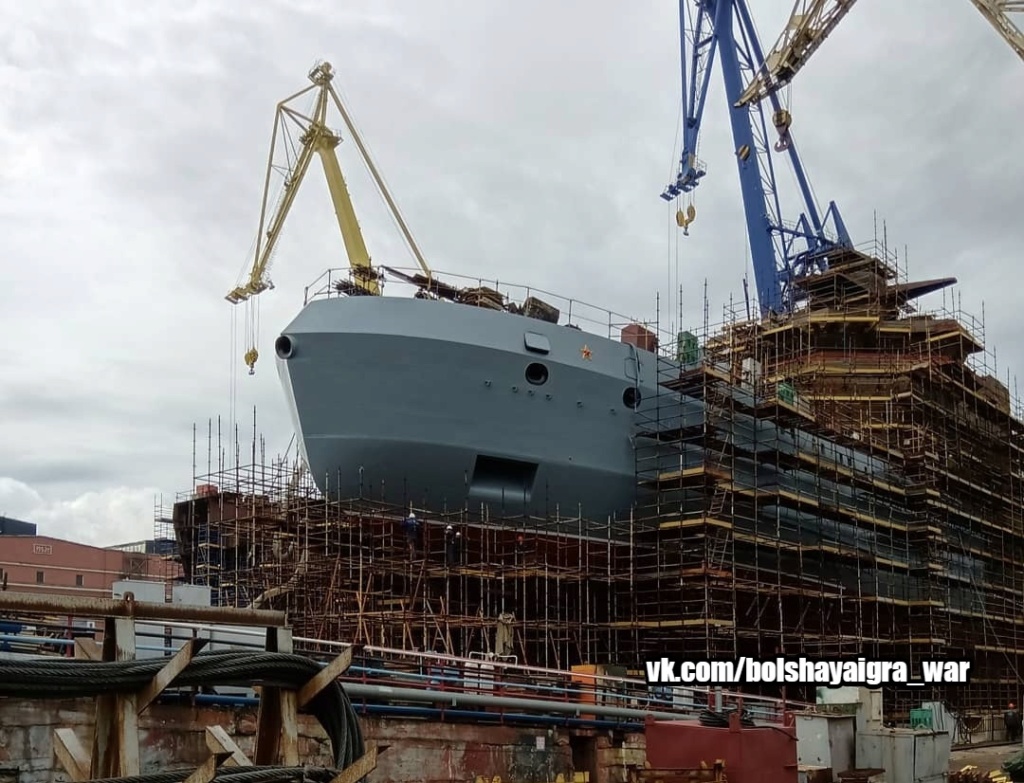
Motor accident on the new nuclear icebreaker "Arctic"
According to the newspaper Kommersant, in the material of Anastasia Vedeneyeva and Ilya Usov, Arktika is losing power. Nuclear-powered icebreaker may be commissioned with a faulty engine ”, one of the propeller electric motors at the Arctic nuclear icebreaker undergoing testing after the breakdown on February 4 was recognized as non-recoverable. This means that the icebreaker, apparently, will have to be docked to replace the engine, which can take at least six months. According to Kommersant’s information, “Rosatom”, in order to avoid prolonged shutdown of the vessel, is considering the option of accepting it with a faulty engine under the shipyard’s obligation to carry out repairs. Then the capacity of the Arctic will temporarily decrease by one third, to 40 MW.
The rowing electric motor (GED) on the right shaft of the Arktika nuclear icebreaker, which broke down in early February during mooring trials, apparently cannot be restored, sources told Kommersant. This is confirmed by the brief information prepared following the results of the meeting of the expanded commission of February 14 (Kommersant has a copy). So, representatives of the Leningrad Electric Machine-Building Plant (LEZ, part of Ruselprom) said it was impossible to restore the operability of the nose winding of the engine (four out of six phases were damaged), the document says. Representatives of the Central Research Institute of Marine Electrical Engineering and Technology (Central Research Institute of Electric Networks, part of the Krylovsky State Research Center), who were involved in the development of the electric propulsion system, believe that the incident was caused by the marriage of the engine. However, in the LEZ (supplier of the HED) the voltage jump from the frequency converter to the HED is blamed.
The Arctic icebreaker has three propeller shafts, each equipped with two 10 MW engines. One of them failed. Two engines on the middle shaft were successfully tested before an incident occurred on February 4 with the HED on the right shaft (see Kommersant on February 10).
If the engine cannot be repaired on board, which now seems most likely, it will be necessary to replace the icebreaker in the dock and open the hull for replacement, which will lead to a significant delay in the delivery of the vessel.
On February 13, the head of the United Shipbuilding Corporation (USC) Alexei Rakhmanov did not directly answer Kommersant’s question whether it is really impossible to fix the engine on board. He only emphasized that the “Arctic” was “a research project, a leading steamboat; this did not exist in the world.” “Nothing catastrophic happened. You can do certain work on board, you can do certain work on the dock, we have all the technological moves written down: we understand what we will do in case A, B, C, ”Mr. Rakhmanov assured. He added that he does not yet see the risks of delaying the transfer of the icebreaker, scheduled for May. In "Rosatom", "Ruselprom" and Krylovsk State Scientific Center until the findings of the commission did not comment on the topic.
According to the source of “b” in the industry, if the cause of what happened was a power surge, this calls into question the correct design of systems. Power surges regularly occur during operation, especially in harsh Arctic conditions, he notes, and frequency converters and fuses are installed to compensate for them. Another interlocutor of Kommersant emphasizes that there are fuses, but they did not save the GED.
One of Kommersant’s sources notes that they have not yet given up their hopes of restoring the GED without cutting the building, and additional experts have been specially involved for this. But another interlocutor claims that the damage of the four phases out of six is very significant: "Most likely, it is pointless to talk about restoration, you need to change the engine, taking into account that the ED housing is not removable, you can not open it and put a patch on it."
According to Kommersant’s interlocutors in the industry, it can take 12–18 months to create a new GED, although theoretically engines that are designed for the following serial icebreakers can be used.
In any case, the replacement of the GED will require considerable time, Kommersant's interlocutors talk about 6-18 months.
However, a number of Kommersant sources do not exclude the possibility that Rosatom may accept an icebreaker with a faulty right GED. Such a solution will also require reducing the load from the left screw, that is, the power will temporarily be 40 MW. Perhaps a legal compromise will be found, and the icebreaker will be accepted under the obligation to eliminate the malfunction in the future, one of Kommersant’s interlocutors notes, otherwise the Arctic will stand for a year by the wall. According to Kommersant’s sources, the test program is ongoing at the icebreaker, despite the breakdown.





 owais.usmani
owais.usmani