+48
limb
Shaun901901
Broski
lyle6
Mir
lancelot
The-thing-next-door
AlfaT8
LMFS
Hole
Rodion_Romanovic
miketheterrible
0nillie0
d_taddei2
Isos
par far
Walther von Oldenburg
galicije83
OminousSpudd
kvs
GunshipDemocracy
BKP
Cyberspec
cracker
sepheronx
Kimppis
Werewolf
George1
Vympel
flamming_python
Zivo
Mike E
Vann7
Asf
franco
VladimirSahin
collegeboy16
TR1
medo
gloriousfatherland
ali.a.r
GarryB
Viktor
Russian Patriot
soldieroffortune
tunguska
Vladislav
Admin
52 posters
Russia Tank Force: Present and Future (Numbers)

Hole- Posts : 11254
Points : 11232
Join date : 2018-03-24
Age : 48
Location : Scholzistan
Yes, new ones will be build.

franco- Posts : 7207
Points : 7233
Join date : 2010-08-18
miketheterrible wrote:Negative on the T-90 since it was mentioned to get around ~500 T-90M tanks. Unless they reopen production of T-90 tanks to build new ones, I think they plant to just upgrade. Unless they are building new ones as well as upgrade.
I wonder if they will decide to upgrade all the T-80's to the BVM designation and send them in the arctic? Would make a great tank for the arctic forces.
T-90's are to be a combination of new (M) and upgrades (AM). The first 60 ordered are 10 new and 50 upgrades. The T-90 is still in production for exports so this will not tax them. Should actually create some foreign sales. They are talking about 300-400 T-80BVM's. No mention if the 200 T-80U's will get an upgrade.

miketheterrible- Posts : 7377
Points : 7333
Join date : 2016-11-06
franco wrote:miketheterrible wrote:Negative on the T-90 since it was mentioned to get around ~500 T-90M tanks. Unless they reopen production of T-90 tanks to build new ones, I think they plant to just upgrade. Unless they are building new ones as well as upgrade.
I wonder if they will decide to upgrade all the T-80's to the BVM designation and send them in the arctic? Would make a great tank for the arctic forces.
T-90's are to be a combination of new (M) and upgrades (AM). The first 60 ordered are 10 new and 50 upgrades. The T-90 is still in production for exports so this will not tax them. Should actually create some foreign sales. They are talking about 300-400 T-80BVM's. No mention if the 200 T-80U's will get an upgrade.
I sure hope they do. Streamlining the tank upgrades is a must to reduce cost and get full potential. The T-80U is past its prime in capabilities and needs the thermal optics and what not.

George1- Posts : 18618
Points : 19121
Join date : 2011-12-22
Location : Greece
Review of the state of the tank forces of the Russian Armed Forces.
On the occasion of the holiday, I dashed off a small reviewer on the topic - the tank troops of the Russian army over the past decade.
ATTENTION !!!! ALL INFORMATION IS TAKEN FROM PUBLIC SOURCES!!!!
As a preface.
The main structural unit of the tank forces is the tank battalion. The battalion consists of three tank companies. Each company consists of three platoons, and each platoon has three tanks. Accordingly, the company has ten tanks (including the company commander's tank), and the battalion thirty-one tanks (including the battalion commander's tank).
The tank fleet of combat units of the Russian army consists of various modifications of three main types - T-72, T-80 and T-90. The most numerous is the T-72B tank. In 1985-1996. the T-72B tank was produced in three versions (T-72B, T-72B1 and T-72B model 1989)
Since 1998, the Uralvagonzavod enterprise has been working to significantly improve the combat capabilities of the T-72B tanks. In 1998-2005. after modernization, the vehicles received the T-72BA index. In 2011-2015. the upgraded vehicles received the T-72B3 index. From 2016 to the present, the updated vehicles, although they continue to wear the T-72B3 index, are seriously different from the tanks of the previous modernization. Unofficially, tanks are indexed T-72B3 of the 2016 model or T-72B3M.
Tanks of the T-80 family are represented in the army by the basic versions of the T-80BV and T-80U (produced in 1983-1998). Since 2005, a number of machines have been modernized and received the T-80BVM and T-80UE-1 indices.
Tanks T-90A (2004-2010) and T-90M (produced since 2019) make up the smallest group in the army.
It should be noted that the tanks of the new production were not supplied to the troops in 2011-2019. and only in 2020 was the first batch of new T-90M vehicles received.
Now let's move on to the list of army units with tank equipment.
NORTHERN FLEET
A separate tank battalion of the 200th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 armed with T-72B tanks, in 2012-2013 re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks, in 2018-2019. rearmed with T-80BVM tanks. WESTERN MILITARY DISTRICT A separate tank battalion of the 138th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 armed with T-72B tanks, in 2012-2013 it was re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 25th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 armed with T-80BV tanks, in 2012 re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 76th Airborne Assault Division - formed in 2019 in service with T-72B3 tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 79th Motorized Rifle Brigade - in 2011, armed with T-72B tanks, in 2020 began rearmament with T-72B3M tanks.
11th Separate Tank Regiment of 11th Army Corps - formed in 2019.There are three tank battalions in total. The 1st battalion is armed with T-72B3 tanks. The other two battalions have not completed their formation and will probably receive T-72B tanks (so far I have not seen photo and video materials). 1st Tank Regiment of the 2nd Motorized Rifle Division - formed in 2016. There are three tank battalions in total. All battalions are armed with T-72B3M tanks. Tank battalion of the 1st motorized rifle regiment of the 2nd motorized rifle division (until 2012, a separate tank battalion of the 5th motorized rifle brigade) - in 2011 armed with T-90A tanks, in 2020 it began rearmament to T-90M tanks. Tank battalion of the 15th motorized rifle regiment of the 2nd motorized rifle division - formed in 2012. It is armed with T-72B3 tanks.
11-72-128-2020-1
A separate tank battalion of the 27th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 in service with T-90A tanks.
12th Panzer Regiment, 4th Panzer Division (until 2012, 4th Panzer Brigade) - A total of three tank battalions. All battalions are armed with T-80U tanks. There are several T-80UE-1 tanks.
13th Panzer Regiment of the 4th Panzer Division - formed in 2012. Only three tank battalions. All battalions are armed with T-80U tanks. There are several T-80UE-1 tanks. Tank battalion of the 423rd Motorized Rifle Regiment of the 4th Tank Division - formed in 2016. It is armed with T-80BV tanks, in 2020 it began rearmament to T-80BVM tanks. 6th Tank Brigade - There are three tank battalions in total. in 2011 in service with the T-80BV tanks. In 2012-2013 she was re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks. In 2018-2019 it was rearmed with T-72B3M tanks.
59th Tank Regiment of 144th Motorized Rifle Division - formed in 2019.There are three tank battalions in total. All battalions are armed with T-72B tanks.
Tank battalion of the 488th motorized rifle regiment of the 144th motorized rifle division (until 2016 a separate tank battalion of the 28th motorized rifle brigade) - in 2011 armed with T-72BA tanks, in 2013 partially re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks. Tank Battalion of the 254th Motorized Rifle Regiment of the 144th Motorized Rifle Division - formed in 2019.The battalion has not completed its formation and will probably receive T-72B tanks (so far I have not seen photo and video materials). 237th Tank Regiment of the 3rd Motorized Rifle Division - formed in 2017. There are only three tank battalions. All battalions are armed with T-72B tanks.
Tank battalion of the 252nd motorized rifle regiment of the 3rd motorized rifle division (until 2016 a separate tank battalion of the 9th motorized rifle brigade) - in 2011 armed with T-80BV tanks, in 2013 re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks. Tank battalion of the 752nd motorized rifle regiment of the 3rd motorized rifle division (until 2016, a separate tank battalion of the 23rd motorized rifle brigade) - in 2011 armed with T-72B tanks. Until 2010, T-72BA tanks were available, but I have not yet come across photo-video materials after 2010. SOUTH MILITARY DISTRICT 68th Tank Regiment of the 150th Motorized Rifle Division - formed in 2016. There are only three tank battalions. All battalions are armed with T-72B3M tanks.
163rd Tank Regiment of the 150th Motorized Rifle Division - formed in 2018.There are three tank battalions in total. All battalions are armed with T-72B tanks.
Tank battalion of the 102nd motorized rifle regiment of the 150th motorized rifle division - formed in 2016. It is armed with T-72B tanks.
The tank battalion of the 103rd motorized rifle regiment of the 150th motorized rifle division is in the stage of formation. It will probably receive the T-72B tanks.
A separate tank battalion of the 20th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 in service with T-90A tanks.
A separate tank battalion of the 136th Motorized Rifle Brigade - in 2011, armed with T-90A tanks.
Tank battalion of the 70th motorized rifle regiment of the 42nd motorized rifle division (until 2017, a separate tank battalion of the 17th motorized rifle brigade) - in 2011, armed with T-72B3 tanks. Tank battalion of the 71st motorized rifle regiment of the 42nd motorized rifle division (until 2017, a separate tank battalion of the 18th motorized rifle brigade) - in 2011, armed with T-72B tanks, in 2013 re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 42nd motorized rifle division - formed in 2017, armed with T-72B3 tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 19th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011, armed with T-90A tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 205th motorized rifle brigade was armed with T-72B tanks in 2011, in 2012-2013 it was re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks.
A separate tank battalion of the 4th military base - in 2011 in service with T-72B tanks.
A separate tank battalion of the 102nd military base - in 2011 armed with T-72B tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 7th Airborne Assault Division - formed in 2019 in service with T-72B3 tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 56th Airborne Assault Brigade - formed in 2019 in service with T-72B3 tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 126th coastal defense brigade - formed in 2014, armed with T-72B3 tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 7th military base - in 2011 armed with T-90A tanks, in 2016 re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks.
A separate tank battalion of the 555th air group in the Syrian Arab Republic - formed in 2015, received the materiel of the battalion of the 7th military base. Armed with T-90A tanks. CENTRAL MILITARY DISTRICT Two separate tank battalions of the 21st motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 armed with T-72BA tanks, in 2013-2014. both battalions were partially re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 35th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011, armed with T-72B tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 74th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 armed with T-72B tanks, in 2014-2015 re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks.
555-90-2015
Tank battalion of the 228th motorized rifle regiment of the 90th tank division (until 2017, a separate tank battalion of the 32nd motorized rifle brigade) - in 2011 armed with T-72BA tanks, in 2020 it began rearmament to T-72B3M tanks ... 239th Tank Regiment, 90th Tank Division (until 2017, 7th Tank Brigade) - There are three tank battalions in total. In 2011, all battalions were armed with T-72B tanks. 6th Tank Regiment of the 90th Panzer Division - formed in 2017. There are three tank battalions in total. All battalions are armed with T-72B tanks. 80th Tank Regiment of the 90th Tank Division - formed in 2017. There are only three tank battalions. All battalions are armed with T-72B tanks.
A separate tank battalion of the 201st military base - formed in 2016 by the merger of three separate tank companies of the base. In 2011, the T-72AV tanks were in service. In 2016, it was partially re-equipped with T-72B tanks. The presence of a separate tank company in the 31st Airborne Assault Brigade has not yet been confirmed by photo and video materials. EASTERN MILITARY DISTRICT. 5th Tank Brigade - There are three tank battalions in total. in 2011 in service with T-72B tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 36th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 in service with T-72B tanks, in 2013-2014. rearmed with T-72B3 tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 37th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 in service with T-72B tanks, in 2013-2014. rearmed with T-72B3 tanks.
A separate tank battalion of the 38th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 armed with T-80BV tanks, in 2013-2014. re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks, in 2019 re-equipped with T-80BV tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 64th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 in service with T-80BV tanks, in 2013-2014. re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks, in 2019 re-equipped with T-80BV tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 69th covering brigade - in 2011 in service with T-80BV tanks, in 2013-2014. re-equipped with T-72B tanks, in 2019 re-equipped with T-80BV tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 39th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 in service with T-80BV tanks, in 2013-2014. re-equipped with T-72B3 tanks, in 2019 re-equipped with T-80BV tanks.
A separate tank battalion of the 57th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011, armed with T-80BV tanks. A separate tank battalion of the 60th motorized rifle brigade - in 2011 in service with T-80BV tanks, in 2013-2014. rearmed with T-72B tanks. Tank battalion of the 114th motorized rifle regiment of the 127th motorized rifle division (until 2019, a separate tank battalion of the 70th motorized rifle brigade) - in 2011 armed with T-80BV tanks, in 2014 re-equipped with T-72B tanks. Tank battalion of the 394th motorized rifle regiment of the 127th motorized rifle division (until 2019, a separate tank battalion of the 59th motorized rifle brigade) - in 2011, armed with T-80BV tanks, in 2014 re-equipped with T-72B tanks. 84th separate tank battalion of the 127th motorized rifle division - formed in 2019, armed with T-72B tanks.
A separate tank company of the 46th machine-gun and artillery regiment of the 18th machine-gun and artillery division - in 2011 armed with T-80BV tanks, in 2014 re-equipped with T-72B tanks.
A separate tank company of the 49th machine-gun and artillery regiment of the 18th machine-gun and artillery division - in 2011 armed with T-80BV tanks, in 2014 re-equipped with T-72B tanks.
A separate tank company of the 83rd Airborne Assault Brigade - formed in 2017 in service with T-72B3 tanks.
A separate tank company of the 40th Marine Brigade - formed in 2018 in service with T-80BV tanks.
A separate tank company of the 155th Marine Brigade - formed in 2019 in service with T-80BV tanks.
155-80-2019-mp4-206400000
The presence of a separate tank company in the 11th Airborne Assault Brigade has not yet been confirmed by photo and video materials.
TRAINING PARTS
training of officers of tank forces is carried out at the Kazan Tank School, at the Omsk Armored Engineering Institute, at the Moscow and Far Eastern Combined Arms Schools. The 212th tank training center, the 56th, 467th, 473rd and 392nd training centers of motorized rifle troops are engaged in training of junior specialists. The total number of training equipment is at least 400 tanks of all brands (with the exception of the T-90M).
THE AFTERWORD
In the past decade, 39 new tank battalions have been formed, with thirty-two of them deployed to the west and south. The total number of deployed tanks almost doubled. To equip new units, in addition to supplies from industry and movements within the districts, it was necessary to transfer new equipment from the brigades of the Central and Eastern military districts. This can explain the obscure leapfrog with the massive removal from service and the subsequent return from storage of T-80BV tanks in a few years.
The tank industry has sharply accelerated the pace of modernization of old machines. If in 1998-2010. about 150 T-72B and T-80U tanks were updated to the level of T-72BA and T-80UE-1, then in 2011-2020. supplies to the troops amounted to more than 600 T-72B3 tanks, more than 300 T-72B3M tanks and more than 60 T-80BVM tanks. After a ten-year hiatus, deliveries of new cars were resumed.
The total staffing of all combat units listed above is 2685 vehicles. The total number of new and modernized tanks (produced in 2000 and later) in combat units is about 1200 units, or about 45 percent of the total.
https://altyn73.livejournal.com/1437693.html
franco, dino00, LMFS and Santu Castigu like this post

franco- Posts : 7207
Points : 7233
Join date : 2010-08-18
Think he may be a little light on the T-72B3's as Shoigu stated there was 1,000 of them upgraded to date... 3 years ago.
EDIT: And they have been upgrading around 200 per year since. In 2020, the totals are projected at 120 T-72B3M, 30-40 T-80BVM, 30-40 T-90M plus some T-14's.
EDIT: And they have been upgrading around 200 per year since. In 2020, the totals are projected at 120 T-72B3M, 30-40 T-80BVM, 30-40 T-90M plus some T-14's.
George1 and miketheterrible like this post

franco- Posts : 7207
Points : 7233
Join date : 2010-08-18
How strong is the firepower of tanks in the combat units of the Russian army?
From a rather interesting article "Review of the state of the tank forces of the Armed Forces of Russia", published on the basis of open sources, it follows that in the combat units of the Russian army in 86 tank battalions there are 2685 tanks of various modifications T-72, T-80, T-90 and more about 400 T-72 tanks in training centers. The composition of the tank fleet by types of tanks and their number in the troops can be presented in the following table.
Based on this information and based on the number and types of tanks in the combat units of the Russian army, it is possible to assess their technical level and capabilities, for example, according to one of the main criteria - the firepower of a tank. Firepower is determined by the main, auxiliary and secondary armament of the tank, the ammunition used and the fire control systems.
All these tanks are equipped with modifications of the 2A46 cannon and the same machine guns as auxiliary and additional weapons. The use of the same gun makes it possible to use on all tanks a full set of existing and promising artillery ammunition, limiting only the length of promising ammunition due to the sweeping of the automatic loader.
The effectiveness of the use of the weapons of these tanks is seriously different in the possibility of conducting effective fire due to the fundamentally different sighting systems of the gunner and commander and the tank's fire control systems.
According to the structure of fire control systems, these tanks can be divided into two groups: the T-72B, T-72BA, T-72B3, T-72B3M family of tanks and the T-80BV, T-8BVM, T-80U, T90A family of tanks.
Firepower of the T-72 family of tanks
The T-72 family of tanks has never had a full-fledged integrated FCS. The concept of sighting systems on them turned out to be far from the best; over time, simplified sights and devices were installed on tanks without serious linking into a single whole. In terms of fire efficiency, they were significantly inferior to the second group of tanks, and this trend extended to the latest models of tanks of this family.
Tanks T-72B and T-72BA are equipped with the simplest sighting systems, laid down in the distant 60s on the T-64A tank. The gunner's sighting system 1A40-1 of the T-72B tank (1985) and the T-72BA tank (1999) is based on the 1K13 sight without stabilization of the field of view with a night channel, providing a range of vision in the passive mode of 500 m and in the active mode of 1200 m. The sight has a built-in laser channel of the Svir guided weapon for firing only from the spot with a 9M119 laser-guided missile at 1200 m at night and at a range of up to 4000 m during the day.
The TPD-K1 sight was left as a backup sight. This is a modification of the TPD-2-49 sight with stabilization of the field of view only vertically, into which a laser rangefinder was built. Instead of TBV, there is a ballistic corrector for entering meteorological ballistic corrections into the sight to develop aiming angles and lateral lead, while the gunner must shift the aiming mark by the lead angle. The commander's sighting system includes the simplest unstabilized day-night sight TKN-3MK with a night vision range of up to 500 m, that is, the commander's ability to detect targets is much worse than that of the gunner.
On the T-72B3 (2011) tank, instead of the 1K13 sight, the Sosna-U multichannel sight with stabilization of the field of view vertically and horizontally is installed, containing an optical and thermal imaging channel with a night vision range of up to 3500 m, a laser guidance channel for the Reflex-M guided missile ", A laser rangefinder and automatic target tracking with the output of the field of view on the gunner's and commander's monitors. The sight provides firing from a standstill and on the move with a Reflex-M rocket at a distance of up to 5000 m.
The ballistic corrector calculates the aiming and lead angles and automatically enters them into the gun drives. At the same time, the Sosna U sight is located to the left of the TPD-K1 sight installed in the most optimal zone of the gunner's work, and when working with a multi-channel sight, it must deflect its body to the left, which creates serious difficulties in its work.
The commander's primitive sighting complex based on the TKN-3MK day-night sight remained unchanged, while duplicate firing from the cannon from the commander's seat was implemented.
On the T-72B3M modification (2014), the commander finally had a perfect sighting system. Instead of TKN-3MK, a panoramic thermal imaging sight PK PAN "Falcon Eye" was installed with two-plane independent stabilization of the field of view, a laser rangefinder, television and thermal imaging channels, providing a range of vision during the day and at night up to 4000 m. The complex provides the commander with all-day and all-weather observation and search for targets, as well as effective firing from a cannon, coaxial and anti-aircraft machine guns.
Firepower of the T-80 and T-90 family of tanks
On another group of tanks (T-80BV, T-80BVM, T-80U and T-90A), a different principle of building an integrated control system was implemented, laid down on the T-64B (1976) and T-80B (1978) tanks and led to implementation on the tank T-80U (1984) the most advanced MSA. The sighting complex of the T-80BV tank includes a gunner's sight "Ob" with a two-plane system of stabilization of the field of view, an optical channel, a laser rangefinder and a receiving channel of the radio command guidance system of the guided missile "Cobra". The digital ballistic computer calculates the aiming and lead angles from weather ballistic data and automatically enters them into the gun drives. The gunner's sight was integrated with the Buran night sight, and the Utes anti-aircraft machine gun was remotely controlled through the TKN-3MK commander's sight.
A more advanced sighting system was installed on the T-80U tank, the Ob gunner's sight was replaced with an improved Irtysh sight with a laser guidance channel for the Reflex missile, and instead of the TKN-3MK commander's sight, the PKN-4S commander's day-night complex was installed with stabilization of the vertical field of view and night infrared channel with a vision range of 1000 m and providing remote control of the anti-aircraft installation and duplicated control of fire from the gun from the commander's seat.
Due to the serious lag of the sighting systems of the T-72 family of tanks on the T-90 tank (1991), it was decided to install the 1A45 gunner's sighting system of the T-80U tank with the Irtysh sight and the Reflex guided weapons and the PKN-4S commander's sighting system , which immediately increased its firepower compared to the T-72B tank.
On the modernized T-90A tank (2006), the sighting system was seriously modernized, instead of the Buran gunner's night sight, a second-generation Essa thermal imager was installed with a night vision range of up to 3500 m and an automatic target tracking. The commander's sighting system has also undergone major changes. Instead of the PKN-4S sighting complex, a PK-5 combined electro-optical sight was installed with independent stabilization of the field of view vertically and horizontally, a laser rangefinder, with television and thermal imaging channels providing a vision range of up to 3000 m. The introduction of a laser rangefinder into the sight allowed the commander to significantly to increase the effectiveness of duplicated firing from a cannon.
Not so long ago, the modernization of the T-80BV tanks to the level of the T-80BVM (2017) began, instead of the Essa thermal imaging sight and the Ob gunner's sight, a modernized Sosna-U multi-channel sight of the latest generation was installed with the replacement of the Cobra guided weapons by the Reflex -M ". It should be noted that all T-80BV tanks are subject to modernization to the T-80BVM level, since the production of the Ob gunner's sights and the Cobra guided weapons complex has long been discontinued.
Prospects for modernizing tanks
Today, only T-72B3M, T-90A, T-80BVM and T-80U tanks (651 out of 2685 tanks) have perfect sighting systems, which is 24% of the total fleet of tanks in combat units, that is, they are seriously inferior in firepower western designs.
A potential adversary has a much better situation in this matter, for a long time, on all modifications of tanks with M1A2 and Leopard 2A2, the gunner has installed multi-channel sights stabilized in two planes with visual and thermal imaging channels and laser rangefinders, and the commander has panoramic multichannel sights with thermal imaging and television channels and laser rangefinders. Sighting systems are linked into a single digital tank control system, which ensures high efficiency of firing.
For Russian tanks, perfect sighting systems for the gunner and commander have already been developed, which are not inferior to Western models, but they have not yet come to their mass introduction on the existing generation of tanks in service. All this suggests that a serious modernization program is required for most of the tanks in combat units. Apparently, it is most advisable to gradually equip these tanks with a single unified Kalina fire control system, which includes a modernized multi-channel gunner's sight Sosna-U and a multichannel panoramic sight of the commander's Falcon Eye, providing all-day and all-weather detection and destruction of targets by the gunner and commander with coordination them into the digital information and control system of the tank. In terms of the effectiveness of firing, these tanks will be close to the level of the Armata tank or at its level.
At the same time, it is worth equipping the existing generation of tanks with a system of network-centric control of tanks on the battlefield and their interaction with a similar system of the Armata tank, which is so necessary at this stage, if it ever reaches the army.
The implementation of such a program largely depends on the capabilities of the industry for the production of component parts and component systems of the tank. In this regard, it is worth considering whether it is necessary to drive mass production of tanks with the same firepower that can be achieved cheaper by upgrading the existing fleet of tanks in the army and many thousands at storage bases.
NOTE: Article written in regards to the one posted previously. IMO the total of upgraded T-72B3, T-72B3M, T-80BVM and T-90M's by the end of this year would be 1600 units plus the 5 battalions of T-90A's.
From a rather interesting article "Review of the state of the tank forces of the Armed Forces of Russia", published on the basis of open sources, it follows that in the combat units of the Russian army in 86 tank battalions there are 2685 tanks of various modifications T-72, T-80, T-90 and more about 400 T-72 tanks in training centers. The composition of the tank fleet by types of tanks and their number in the troops can be presented in the following table.
Based on this information and based on the number and types of tanks in the combat units of the Russian army, it is possible to assess their technical level and capabilities, for example, according to one of the main criteria - the firepower of a tank. Firepower is determined by the main, auxiliary and secondary armament of the tank, the ammunition used and the fire control systems.
All these tanks are equipped with modifications of the 2A46 cannon and the same machine guns as auxiliary and additional weapons. The use of the same gun makes it possible to use on all tanks a full set of existing and promising artillery ammunition, limiting only the length of promising ammunition due to the sweeping of the automatic loader.
The effectiveness of the use of the weapons of these tanks is seriously different in the possibility of conducting effective fire due to the fundamentally different sighting systems of the gunner and commander and the tank's fire control systems.
According to the structure of fire control systems, these tanks can be divided into two groups: the T-72B, T-72BA, T-72B3, T-72B3M family of tanks and the T-80BV, T-8BVM, T-80U, T90A family of tanks.
Firepower of the T-72 family of tanks
The T-72 family of tanks has never had a full-fledged integrated FCS. The concept of sighting systems on them turned out to be far from the best; over time, simplified sights and devices were installed on tanks without serious linking into a single whole. In terms of fire efficiency, they were significantly inferior to the second group of tanks, and this trend extended to the latest models of tanks of this family.
Tanks T-72B and T-72BA are equipped with the simplest sighting systems, laid down in the distant 60s on the T-64A tank. The gunner's sighting system 1A40-1 of the T-72B tank (1985) and the T-72BA tank (1999) is based on the 1K13 sight without stabilization of the field of view with a night channel, providing a range of vision in the passive mode of 500 m and in the active mode of 1200 m. The sight has a built-in laser channel of the Svir guided weapon for firing only from the spot with a 9M119 laser-guided missile at 1200 m at night and at a range of up to 4000 m during the day.
The TPD-K1 sight was left as a backup sight. This is a modification of the TPD-2-49 sight with stabilization of the field of view only vertically, into which a laser rangefinder was built. Instead of TBV, there is a ballistic corrector for entering meteorological ballistic corrections into the sight to develop aiming angles and lateral lead, while the gunner must shift the aiming mark by the lead angle. The commander's sighting system includes the simplest unstabilized day-night sight TKN-3MK with a night vision range of up to 500 m, that is, the commander's ability to detect targets is much worse than that of the gunner.
On the T-72B3 (2011) tank, instead of the 1K13 sight, the Sosna-U multichannel sight with stabilization of the field of view vertically and horizontally is installed, containing an optical and thermal imaging channel with a night vision range of up to 3500 m, a laser guidance channel for the Reflex-M guided missile ", A laser rangefinder and automatic target tracking with the output of the field of view on the gunner's and commander's monitors. The sight provides firing from a standstill and on the move with a Reflex-M rocket at a distance of up to 5000 m.
The ballistic corrector calculates the aiming and lead angles and automatically enters them into the gun drives. At the same time, the Sosna U sight is located to the left of the TPD-K1 sight installed in the most optimal zone of the gunner's work, and when working with a multi-channel sight, it must deflect its body to the left, which creates serious difficulties in its work.
The commander's primitive sighting complex based on the TKN-3MK day-night sight remained unchanged, while duplicate firing from the cannon from the commander's seat was implemented.
On the T-72B3M modification (2014), the commander finally had a perfect sighting system. Instead of TKN-3MK, a panoramic thermal imaging sight PK PAN "Falcon Eye" was installed with two-plane independent stabilization of the field of view, a laser rangefinder, television and thermal imaging channels, providing a range of vision during the day and at night up to 4000 m. The complex provides the commander with all-day and all-weather observation and search for targets, as well as effective firing from a cannon, coaxial and anti-aircraft machine guns.
Firepower of the T-80 and T-90 family of tanks
On another group of tanks (T-80BV, T-80BVM, T-80U and T-90A), a different principle of building an integrated control system was implemented, laid down on the T-64B (1976) and T-80B (1978) tanks and led to implementation on the tank T-80U (1984) the most advanced MSA. The sighting complex of the T-80BV tank includes a gunner's sight "Ob" with a two-plane system of stabilization of the field of view, an optical channel, a laser rangefinder and a receiving channel of the radio command guidance system of the guided missile "Cobra". The digital ballistic computer calculates the aiming and lead angles from weather ballistic data and automatically enters them into the gun drives. The gunner's sight was integrated with the Buran night sight, and the Utes anti-aircraft machine gun was remotely controlled through the TKN-3MK commander's sight.
A more advanced sighting system was installed on the T-80U tank, the Ob gunner's sight was replaced with an improved Irtysh sight with a laser guidance channel for the Reflex missile, and instead of the TKN-3MK commander's sight, the PKN-4S commander's day-night complex was installed with stabilization of the vertical field of view and night infrared channel with a vision range of 1000 m and providing remote control of the anti-aircraft installation and duplicated control of fire from the gun from the commander's seat.
Due to the serious lag of the sighting systems of the T-72 family of tanks on the T-90 tank (1991), it was decided to install the 1A45 gunner's sighting system of the T-80U tank with the Irtysh sight and the Reflex guided weapons and the PKN-4S commander's sighting system , which immediately increased its firepower compared to the T-72B tank.
On the modernized T-90A tank (2006), the sighting system was seriously modernized, instead of the Buran gunner's night sight, a second-generation Essa thermal imager was installed with a night vision range of up to 3500 m and an automatic target tracking. The commander's sighting system has also undergone major changes. Instead of the PKN-4S sighting complex, a PK-5 combined electro-optical sight was installed with independent stabilization of the field of view vertically and horizontally, a laser rangefinder, with television and thermal imaging channels providing a vision range of up to 3000 m. The introduction of a laser rangefinder into the sight allowed the commander to significantly to increase the effectiveness of duplicated firing from a cannon.
Not so long ago, the modernization of the T-80BV tanks to the level of the T-80BVM (2017) began, instead of the Essa thermal imaging sight and the Ob gunner's sight, a modernized Sosna-U multi-channel sight of the latest generation was installed with the replacement of the Cobra guided weapons by the Reflex -M ". It should be noted that all T-80BV tanks are subject to modernization to the T-80BVM level, since the production of the Ob gunner's sights and the Cobra guided weapons complex has long been discontinued.
Prospects for modernizing tanks
Today, only T-72B3M, T-90A, T-80BVM and T-80U tanks (651 out of 2685 tanks) have perfect sighting systems, which is 24% of the total fleet of tanks in combat units, that is, they are seriously inferior in firepower western designs.
A potential adversary has a much better situation in this matter, for a long time, on all modifications of tanks with M1A2 and Leopard 2A2, the gunner has installed multi-channel sights stabilized in two planes with visual and thermal imaging channels and laser rangefinders, and the commander has panoramic multichannel sights with thermal imaging and television channels and laser rangefinders. Sighting systems are linked into a single digital tank control system, which ensures high efficiency of firing.
For Russian tanks, perfect sighting systems for the gunner and commander have already been developed, which are not inferior to Western models, but they have not yet come to their mass introduction on the existing generation of tanks in service. All this suggests that a serious modernization program is required for most of the tanks in combat units. Apparently, it is most advisable to gradually equip these tanks with a single unified Kalina fire control system, which includes a modernized multi-channel gunner's sight Sosna-U and a multichannel panoramic sight of the commander's Falcon Eye, providing all-day and all-weather detection and destruction of targets by the gunner and commander with coordination them into the digital information and control system of the tank. In terms of the effectiveness of firing, these tanks will be close to the level of the Armata tank or at its level.
At the same time, it is worth equipping the existing generation of tanks with a system of network-centric control of tanks on the battlefield and their interaction with a similar system of the Armata tank, which is so necessary at this stage, if it ever reaches the army.
The implementation of such a program largely depends on the capabilities of the industry for the production of component parts and component systems of the tank. In this regard, it is worth considering whether it is necessary to drive mass production of tanks with the same firepower that can be achieved cheaper by upgrading the existing fleet of tanks in the army and many thousands at storage bases.
NOTE: Article written in regards to the one posted previously. IMO the total of upgraded T-72B3, T-72B3M, T-80BVM and T-90M's by the end of this year would be 1600 units plus the 5 battalions of T-90A's.
GarryB, George1 and LMFS like this post

LMFS- Posts : 5230
Points : 5226
Join date : 2018-03-03
Original source and referred table:
https://naspravdi.info/novosti/naskolko-silna-ognevaya-moshch-tankov-v-stroevyh-chastyah-rossiyskoy-armii
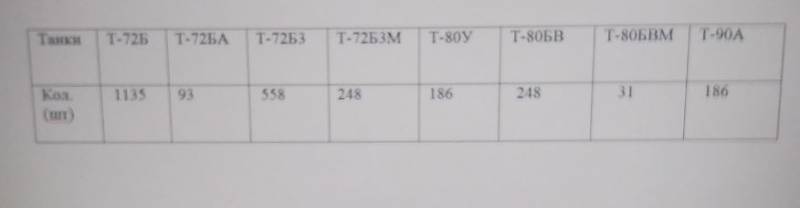
https://naspravdi.info/novosti/naskolko-silna-ognevaya-moshch-tankov-v-stroevyh-chastyah-rossiyskoy-armii


franco- Posts : 7207
Points : 7233
Join date : 2010-08-18
Update notes:
1. Did some further research on the number of T-72B3 and T-72B3M's upgrades with various Russian and foreign sources with the general consensus being about 1500 total by year's end. The ratio appears to be 1100-1150 T-72B3's and 350-400 T-72B3M's. Have also been monitoring mentions of tank types during exercises by the Defense Ministry and some of the units mentioned in the article above are being mentioned as having T-72B3's instead of the article quoted types.
2. The original upgrade to the T-72 was known as the T-72BM or T-72B1 or T-72B2 depending on the source and there were just over 150 of them produced around 2009-2011 before being discontinued for the T-72B3. So there are 5 battalions of them operational in addition.
3. There seemed to be some general confusion in regards to where the second battalion of the T-80BVM was going to. It went to the 4th Tank Division instead of the 38th Brigade out in Amur. The 38th Brigade was also reported to have received new T-80BV(M)'s. While researching the T-72B3's was reminded by the Swedish Defense Institutes equipment delivery totals of the arrival of 115 upgraded T-80BV's around 2011. They were obviously put into storage as the decision at that time was to go with the T-72's only. Noticed in Defense Ministry's press releases for this summer military exercises, some units like the 38th are referred to as using improved T-80BV's. The 115 tanks would be enough to equipment 3 battalions and 2 companies. Suspect the battalions to be the tank units of the 38th, 69th and 57th Motor Rifle brigades and the 2 companies are the 40th and 155th Naval Infantry brigades. What the improvement is over a regular T-80BV not sure?
4. As a side note out in the Eastern Command, the 36th, 37th, 39th and 64th Motor Rifle Brigades were all reported to be T-72B3's by the Defense Ministry and the 5th Tank brigade were T-72B's.
1. Did some further research on the number of T-72B3 and T-72B3M's upgrades with various Russian and foreign sources with the general consensus being about 1500 total by year's end. The ratio appears to be 1100-1150 T-72B3's and 350-400 T-72B3M's. Have also been monitoring mentions of tank types during exercises by the Defense Ministry and some of the units mentioned in the article above are being mentioned as having T-72B3's instead of the article quoted types.
2. The original upgrade to the T-72 was known as the T-72BM or T-72B1 or T-72B2 depending on the source and there were just over 150 of them produced around 2009-2011 before being discontinued for the T-72B3. So there are 5 battalions of them operational in addition.
3. There seemed to be some general confusion in regards to where the second battalion of the T-80BVM was going to. It went to the 4th Tank Division instead of the 38th Brigade out in Amur. The 38th Brigade was also reported to have received new T-80BV(M)'s. While researching the T-72B3's was reminded by the Swedish Defense Institutes equipment delivery totals of the arrival of 115 upgraded T-80BV's around 2011. They were obviously put into storage as the decision at that time was to go with the T-72's only. Noticed in Defense Ministry's press releases for this summer military exercises, some units like the 38th are referred to as using improved T-80BV's. The 115 tanks would be enough to equipment 3 battalions and 2 companies. Suspect the battalions to be the tank units of the 38th, 69th and 57th Motor Rifle brigades and the 2 companies are the 40th and 155th Naval Infantry brigades. What the improvement is over a regular T-80BV not sure?
4. As a side note out in the Eastern Command, the 36th, 37th, 39th and 64th Motor Rifle Brigades were all reported to be T-72B3's by the Defense Ministry and the 5th Tank brigade were T-72B's.
miketheterrible, LMFS and lyle6 like this post

LMFS- Posts : 5230
Points : 5226
Join date : 2018-03-03
A new batch of 10 T-72B3M was delivered these days to the Central MD:
https://en.topwar.ru/176159-partija-modernizirpovannyh-tankov-t-72b3m-postupila-v-cvo.html
https://en.topwar.ru/176159-partija-modernizirpovannyh-tankov-t-72b3m-postupila-v-cvo.html

franco- Posts : 7207
Points : 7233
Join date : 2010-08-18
LMFS wrote:A new batch of 10 T-72B3M was delivered these days to the Central MD:
https://en.topwar.ru/176159-partija-modernizirpovannyh-tankov-t-72b3m-postupila-v-cvo.html
Believe that to be the 3rd company of the Motor Rifle's Regiment tank battalion, so their conversion is complete. One of the 3 Tank regiments have T-72B3's while the other two still have T-72B's.
LMFS likes this post

AlfaT8- Posts : 2519
Points : 2510
Join date : 2013-02-02
TMA1 likes this post

GarryB- Posts : 41148
Points : 41650
Join date : 2010-03-30
Location : New Zealand
Blah blah blah... the fact that the upgraded T-72s don't have the same level of armour as western first line best available tanks is amusing... the guy who did the video does know Russia has a lot of territory that doesn't face HATO countries and would not normally face them in conflict... and comparing armour with armour is juvenile... you should compare armour with anti armour weapons and with new ARENA and ERA even the upgraded T-72 should be fine.
The video starts with War Thunder, so this guy should realise that when he talks about good armour it means nothing in real combat because every tank in the world is like a man with a shield to stand behind that will stop pistol bullets with everyone armed with pistols or SMG... he can face one person with his shield and fire at them but anyone from his flank or rear can kill him fairly easily... and of course you can't just push a button to put out all fires and repair serious internal damage by holding a button and waiting 30 seconds. Tracks don't fix themselves either... and the Russians have an enormous range of very capable anti armour missiles of a wide range of types plus the air defence capacity to protect their armoured units from at least some drones and enemy air threats... unlike HATO which would be screwed because they expect their fighters to clear the skies...
The video starts with War Thunder, so this guy should realise that when he talks about good armour it means nothing in real combat because every tank in the world is like a man with a shield to stand behind that will stop pistol bullets with everyone armed with pistols or SMG... he can face one person with his shield and fire at them but anyone from his flank or rear can kill him fairly easily... and of course you can't just push a button to put out all fires and repair serious internal damage by holding a button and waiting 30 seconds. Tracks don't fix themselves either... and the Russians have an enormous range of very capable anti armour missiles of a wide range of types plus the air defence capacity to protect their armoured units from at least some drones and enemy air threats... unlike HATO which would be screwed because they expect their fighters to clear the skies...
lyle6 likes this post

The-thing-next-door- Posts : 1455
Points : 1513
Join date : 2017-09-18
Location : Uranus
Funnily enough in warthunder the T-72B-3 is better than the m1a2 because of it having better hull armor and lacking the abrams centre of mass weakspot.
If you hit the abrams below the turret armor it will be perforated and in that game it is hit more often than not.
Another funny thing is that when using a helicopter is is very normal to hit the thin sheet metal upper plate and especially if you use the automatic targeting.
I think the leopard 2 is slightly better, but it's hull armor is still poor and if hit in the hull it will either be ammunition or both the driver and gunner that are hit.
I find it funny that the demented retards who spread western propaganda are always claiming that "cramped" interiors of Soviet tanks result in low crew survivability, when in fact western tanks line up multiple crew members in a row and Russian tanks place them as far apart as possible. Add to that ofcourse that your probability of getting hit is the exact same weather you are in a small tanks or the bloody maus.
If you hit the abrams below the turret armor it will be perforated and in that game it is hit more often than not.
Another funny thing is that when using a helicopter is is very normal to hit the thin sheet metal upper plate and especially if you use the automatic targeting.
I think the leopard 2 is slightly better, but it's hull armor is still poor and if hit in the hull it will either be ammunition or both the driver and gunner that are hit.
I find it funny that the demented retards who spread western propaganda are always claiming that "cramped" interiors of Soviet tanks result in low crew survivability, when in fact western tanks line up multiple crew members in a row and Russian tanks place them as far apart as possible. Add to that ofcourse that your probability of getting hit is the exact same weather you are in a small tanks or the bloody maus.
GarryB and TMA1 like this post

GarryB- Posts : 41148
Points : 41650
Join date : 2010-03-30
Location : New Zealand
It is the same with stealth... the max stealth figure is given as something important... like saying the Leopard 2 has 2.5m of armour when it clearly cannot fit that much armour in the space available.
The simple fact is that even the Maus didn't have enough armour to be impervious and any rivers or just a deep ditch dug by the locals could have immobilised it.
Tanks are not about one feature or another, they are about a range of features that together either make a good tank or a bad tank, and there is no such thing as a universally perfect tank. By any rating system every tank will have areas of strength and areas of relative weakness. Not having the most powerful engines is not a weakness if you already have the lightest tank by 20 tons.
Good power is a good thing and the more powerful the engine the better, but not having the most powerful engine does not make the tank bad.
As the US has found the cost of having the highest level of stealth is enormous to the point of making an all stealth fighter fleet unaffordable to the worlds most powerful military that likes to spend money on defence...
War thunder tries to model penetration and armour performance accurately, but repair is totally unrealistic and of course communication and tactics don't exist in the game... a combined force that works together will always trash a force that might be bigger and might even be better equipped...
The simple fact is that even the Maus didn't have enough armour to be impervious and any rivers or just a deep ditch dug by the locals could have immobilised it.
Tanks are not about one feature or another, they are about a range of features that together either make a good tank or a bad tank, and there is no such thing as a universally perfect tank. By any rating system every tank will have areas of strength and areas of relative weakness. Not having the most powerful engines is not a weakness if you already have the lightest tank by 20 tons.
Good power is a good thing and the more powerful the engine the better, but not having the most powerful engine does not make the tank bad.
As the US has found the cost of having the highest level of stealth is enormous to the point of making an all stealth fighter fleet unaffordable to the worlds most powerful military that likes to spend money on defence...
War thunder tries to model penetration and armour performance accurately, but repair is totally unrealistic and of course communication and tactics don't exist in the game... a combined force that works together will always trash a force that might be bigger and might even be better equipped...
lyle6 likes this post

flamming_python- Posts : 9810
Points : 9868
Join date : 2012-01-30
He is aware that Germany still has Leo-1 tanks in service?
That the US still has more baseline M1A1 Abrams tanks than any of their later mods, and that the tank design itself is virtually as old as the T-80?
I'm trying to figure out what he's talking about, what foreign tanks is he comparing the T-80BVM and T-72B3M to precisely? They're more than a match for 90% of tanks in service around the world, and the remaining 10% they're still quite capable of beating.
That the US still has more baseline M1A1 Abrams tanks than any of their later mods, and that the tank design itself is virtually as old as the T-80?
I'm trying to figure out what he's talking about, what foreign tanks is he comparing the T-80BVM and T-72B3M to precisely? They're more than a match for 90% of tanks in service around the world, and the remaining 10% they're still quite capable of beating.
GarryB likes this post

Isos- Posts : 11668
Points : 11634
Join date : 2015-11-06
flamming_python wrote:He is aware that Germany still has Leo-1 tanks in service?
That the US still has more baseline M1A1 Abrams tanks than any of their later mods, and that the tank design itself is virtually as old as the T-80?
I'm trying to figure out what he's talking about, what foreign tanks is he comparing the T-80BVM and T-72B3M to precisely? They're more than a match for 90% of tanks in service around the world, and the remaining 10% they're still quite capable of beating.
Leo 1 is no more in service. They have less than 400 leo 2 in service. Looking how tanks get easily destroyed in modern warfare thry will end up with no tank after the 1st week of fighting. Some destroyed by air force, some by drones, some by suicide drones, some by athm, some in their parkings by iskanders...
If you want to use tanks you better have 2000 of them and rush quickly to take enemy country. Because if you have only 200-300 you'll see them destroyed pretty easily. Even groups of paramilitary/guerillas can know get enough atgm/drones to destroy such number easily.
Well it's true for any vehicle.
Best weapon today is the trained soldier on foot with very good equipment.

The-thing-next-door- Posts : 1455
Points : 1513
Join date : 2017-09-18
Location : Uranus
flamming_python wrote:
That the US still has more baseline M1A1 Abrams tanks than any of their later mods, and that the tank design itself is virtually as old as the T-80?
And the armor estimates given are quite likely subject to the exact same bias as any other characteristics of the the so called best fighting force in the world's cheaply made for profit garbage.
I would hardly be surprised if thier turret fronts were pierced by 3bm42 rounds at maximum range.
I'm trying to figure out what he's talking about, what foreign tanks is he comparing the T-80BVM and T-72B3M to precisely? They're more than a match for 90% of tanks in service around the world, and the remaining 10% they're still quite capable of beating.
He always cites tanks that are not in service like the leopard 2a7 and m1a3 although judging by the extent to which he claims that western tanks are superior it seems he is really comparing them to theoretical tanks with 130 and 140 mm guns aswell as stolen Soviet APS and autoloader tech.
It is like comparing the m1a1 to the Object-195 and Object477 and claiming that it is obsolete because it will not stand up to 180mm magnetic accelerator cannon.
For most application the T-72B3 is adequate and it atleast matches most to the tanks the west could currently throw at it in any significant numbers. After all the existence of a few tigers did not stopped the T-34's from getting all the way to berlin.

GarryB- Posts : 41148
Points : 41650
Join date : 2010-03-30
Location : New Zealand
The US obliterates third world countries because of the coordination and communication and the superior tactics and often the ability to fight at night.
Well for Russian units that don't have great night vision they can set up defensive positures at night and operate during the day.
Good quality night vision equipment is developing and spreading through the Russian military... all their tanks might not have thermal imagers but many of the anti tank guided missile teams have them as standard, which means they will be very powerful defensively at night because an ATGM 4km away is a tricky target anyway, and with Kornet reaching 6km, and Kornet EM reaching 8.5km those rampaging HATO tanks are going to be very careful how they pick their way forward...
Well for Russian units that don't have great night vision they can set up defensive positures at night and operate during the day.
Good quality night vision equipment is developing and spreading through the Russian military... all their tanks might not have thermal imagers but many of the anti tank guided missile teams have them as standard, which means they will be very powerful defensively at night because an ATGM 4km away is a tricky target anyway, and with Kornet reaching 6km, and Kornet EM reaching 8.5km those rampaging HATO tanks are going to be very careful how they pick their way forward...

franco- Posts : 7207
Points : 7233
Join date : 2010-08-18
The defense of the Kuril Islands will be strengthened with modernized T-72B3 tanks . The corresponding decision was made by the Ministry of Defense, Izvestia reports with reference to the military department.
As the newspaper writes, the first tanks entered service with the units responsible for the defense of the islands in the summer of this year. Before that, the crews of the machines mastered the equipment on simulators, after its arrival, commissioning and familiarization, control firing was carried out with the implementation of practical exercises.
The Ministry of Defense plans that the complete rearmament and mastering of new equipment by personnel will take one to two years.
The press service of the BBO clarified that the 68th Army Corps, whose headquarters is located in Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, is responsible for the defense of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands. Units of the 18th machine-gun and artillery division, which includes a separate tank battalion, are located directly on the Kuril Islands. In addition, there are tank units in the machine-gun and artillery regiments.
T-72B3M is a deeply modernized version of the T-72 main battle tank. The T-72B3 is equipped with more powerful engines of 1130 hp, an improved fire control system with a digital ballistic computer, a sight with a laser rangefinder and an anti-tank missile control system, and digital communications of the latest generation. In addition, tanks are equipped with a rearview camera to facilitate reversing.
The armor of the T-72B3 is reinforced with side screens with "Relikt" reactive armor modules, hinged lattice screens, as well as new reactive armor systems in a "soft" hull.
NOTE: talk was of these units receiving the T-80BVM due to the harsh winters however apparently another route was decided. The 39th Motor Rifle Brigade covering Sakhalin is already reported to be using the T-72B3.
EDIT: just noticed a MO press release about these Kuril units and T-80's were mentioned. So presently probably T-80B or BV's switching to T-72B3's.
As the newspaper writes, the first tanks entered service with the units responsible for the defense of the islands in the summer of this year. Before that, the crews of the machines mastered the equipment on simulators, after its arrival, commissioning and familiarization, control firing was carried out with the implementation of practical exercises.
The Ministry of Defense plans that the complete rearmament and mastering of new equipment by personnel will take one to two years.
The press service of the BBO clarified that the 68th Army Corps, whose headquarters is located in Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, is responsible for the defense of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands. Units of the 18th machine-gun and artillery division, which includes a separate tank battalion, are located directly on the Kuril Islands. In addition, there are tank units in the machine-gun and artillery regiments.
T-72B3M is a deeply modernized version of the T-72 main battle tank. The T-72B3 is equipped with more powerful engines of 1130 hp, an improved fire control system with a digital ballistic computer, a sight with a laser rangefinder and an anti-tank missile control system, and digital communications of the latest generation. In addition, tanks are equipped with a rearview camera to facilitate reversing.
The armor of the T-72B3 is reinforced with side screens with "Relikt" reactive armor modules, hinged lattice screens, as well as new reactive armor systems in a "soft" hull.
NOTE: talk was of these units receiving the T-80BVM due to the harsh winters however apparently another route was decided. The 39th Motor Rifle Brigade covering Sakhalin is already reported to be using the T-72B3.
EDIT: just noticed a MO press release about these Kuril units and T-80's were mentioned. So presently probably T-80B or BV's switching to T-72B3's.
Last edited by franco on Wed Oct 28, 2020 2:31 pm; edited 1 time in total

LMFS- Posts : 5230
Points : 5226
Join date : 2018-03-03
Russian grouping in the Kaliningrad region has been reinforced with 30 modernized tanks
28.10.2020 14:15:39
Moscow. 28 of October. INTERFAX - The army corps stationed in the Kaliningrad region received 30 modernized T-72B3M tanks, the press service of the Russian Baltic Fleet said on Wednesday.
"In 2020, 30 T-72B3M tanks with improved combat characteristics entered service with the motorized rifle unit of the army corps of the Baltic Fleet stationed in the Kaliningrad region. The new equipment will increase the combat capabilities of the compound due to improved maneuverability and armor protection of the crew," the statement said.
The military reported that all the tanks that arrived in the Kaliningrad region left the assembly line of Uralvagonzavod in 2019.
https://www.militarynews.ru/story.asp%3Frid%3D1%26nid%3D540735%26lang%3DRU
28.10.2020 14:15:39
Moscow. 28 of October. INTERFAX - The army corps stationed in the Kaliningrad region received 30 modernized T-72B3M tanks, the press service of the Russian Baltic Fleet said on Wednesday.
"In 2020, 30 T-72B3M tanks with improved combat characteristics entered service with the motorized rifle unit of the army corps of the Baltic Fleet stationed in the Kaliningrad region. The new equipment will increase the combat capabilities of the compound due to improved maneuverability and armor protection of the crew," the statement said.
The military reported that all the tanks that arrived in the Kaliningrad region left the assembly line of Uralvagonzavod in 2019.
https://www.militarynews.ru/story.asp%3Frid%3D1%26nid%3D540735%26lang%3DRU
franco, medo and PapaDragon like this post

George1- Posts : 18618
Points : 19121
Join date : 2011-12-22
Location : Greece
Supplies of Tanks to the Russian Armed Forces in 2020
A total of 300 tanks of all types are planned to be delivered per year.
https://function.mil.ru/news_page/country/more.htm?id=12323601@egNews
T-90M
in November and April in two batches (at least 20 tanks) were delivered to re-equip a tank battalion 1st Motorized Rifle Regiment, 2nd Motorized Rifle Division
https://function.mil.ru/news_page/country/more.htm?id=12286544@egNews
https://tvzvezda.ru/news/opk/content/202011261816-sDTHD.html
In November, a batch of (about ten) tanks was delivered to the Kazan Tank School
https://tvzvezda.ru/news /opk/content/202011261816-sDTHD.html
T-80BVM
In August, the tank battalion of the 423rd motorized rifle regiment of the 4th tank division received ten T-80BVM tanks
https://function.mil.ru/news_page/country/more.htm ? id = 12305044 @ egNews
In November, a batch of tanks was delivered to the Kazan Tank School
https://tvzvezda.ru/news/opk/content/202011261816-sDTHD.html
T-72B3M (sample 2016)
120 tanks were planned for the year
https://function.mil.ru/news_page/country/more.htm?id=12289931@egNews
In August, the re-equipment of the tank battalion of the 79th motorized rifle brigade was completed. A total of 30 T-72B3M tanks were delivered
https://function.mil.ru/news_page/country/more.htm?id=12321709@egNews
https://function.mil.ru/news_page/country/more.htm?id= 12309258 @ egNews
Since April, the tank battalion of the 228th motorized rifle regiment and two tank battalions of the 239th tank regiment of the 90th tank division are being re-equipped
https://function.mil.ru/ news_page/country/more.htm?id=12319319@egNews
new tanks of the 239th tank regiment
new tanks of the 228th motorized rifle regiment
In November, a batch of tanks was delivered to the Kazan Tank School
https://tvzvezda.ru/news/opk/content/202011261816-sDTHD.html
In the fall, a batch of tanks was delivered to the Novosibirsk Military School
https://youtu.be/659rEveatgg
Tanks T-72B and T-80BV received from storage.
To equip four tank battalions newly created in 2020 (one in the 150th motorized rifle division and three in the 127th motorized rifle division), T-72B tanks taken from storage were used, about 120 vehicles in total. Probably, the equipment of two tank battalions of the 11th separate tank regiment was carried out by transferring T-72B tanks from other units.
It should be noted that even old T-72A tanks are removed from storage to equip new parts. This can be seen in the footage of the video about the exercise of the 80th Panzer Regiment of the 90th Panzer Division this summer, where T-72A tanks of the early series are flashing.
I did not come across information on the supply of T-80BV tanks removed from storage. In total, 300 tanks were delivered to the troops in 2020 (180 new and upgraded plus 120 removed from storage).
https://bmpd.livejournal.com/4211202.html
GarryB, LMFS and Hole like this post

lancelot- Posts : 3190
Points : 3186
Join date : 2020-10-18
All these tanks being taken out of storage. Is Russia expecting major border friction?
I would have expected them to upgrade existing units to improve capabilities rather than creating whole new units with equipment from stocks.
I would have expected them to upgrade existing units to improve capabilities rather than creating whole new units with equipment from stocks.

franco- Posts : 7207
Points : 7233
Join date : 2010-08-18
lancelot wrote:All these tanks being taken out of storage. Is Russia expecting major border friction?
I would have expected them to upgrade existing units to improve capabilities rather than creating whole new units with equipment from stocks.
Those units you heard were formed over the last few years are still filling out with men and equipment. This year alone there were two Motor Rifle regiments and one tank regiment started. Last year 2 Motor Rifle regiments and 5 Tank regiments. Most of these units would receive older equipment as they receive staff, organize and train. Meanwhile the other units continue to get modern equipment. As an example the 144th Division was formed a couple of years ago. Still not sure if the Tank regiment is fully formed, same with the 150th which formed later. Both Motor Rifle regiments appear to be fully operational there now but not sure about the second Tank regiment.
DerWolf and LMFS like this post

flamming_python- Posts : 9810
Points : 9868
Join date : 2012-01-30
- Post n°199
 Specialization in tank companies?
Specialization in tank companies?
I was reading some material about the Battle of Kursk, and it was mentioned that about 7-8% of the German tank pool consisted of Tiger tanks (with a similar number of Panthers).
One smart thing the Germans did at the battle, was not to group their Tigers up into their own formations, but spread them around all the existing tank formations. What you ended up with was tank companies and groups consisting of multiple different types of tanks, including the Tigers. The Tigers would spearhead each assault and moving column, and would essentially act as shields for the tanks behind them.
This mitigated the effect and tactics of Soviet AT artillery very significantly. The Soviet 76mm AT guns could only reliably penetrate a Tiger frontally from about 300m. Thus upon sighting the presence of Tigers in an advancing formation, they could not open fire at 1-2km, but had to wait until the tanks were nearly on top of them - even if the majority of the German force otherwise consisted of Panzer IIIs and IVs. If the AT grouping were successful in concealment until then, they would usually knock out some tanks, but the position would ultimately be overrun.
It was a similar story for the T-34s entrenched in defensive positions.
The Soviet 45mm guns meanwhile, which made up more of the Soviet AT force than anything else - were not very effective against even German medium tanks on a good day, and stood no chance against Panthers and Tigers. Thus they were discouraged from engaging at all, and could only rely on ambush tactics.
The end result is that barely any Soviet AT guns had survived to the end of the German offensive, and the start of the Soviet attempted counterattack.
Anyway this got me all thinking
What would be the feasibility of mixing up tank companies today and creating specializations within them, so that there is a counter to any tactic the enemy wants to adopt?
AFAIK nothing like this concept is employed in either the Russian tank force or the NATO formations today.
Taking for example a T-72B3 company.
The command tank could be equipped with an APS and the very latest reactive armour. Possibly along with it another tank could be equipped the same way as well. This would not only afford more protection to the most crucial tank in the formation, but would discourage the enemy from engaging at all, if they knew that what they had was unable to penetrate the lead tank's protection.
Taking the concept further, another T-72B3 of the company, could instead be swapped out for a BMPT-72, and would be used to suppress AT positions, infantry in dug-outs, bunkers or buildings.
Another tank could be fitted with a bias towards tank-launched missiles as opposed to normal rounds, and fitted with more sophisticated thermal and conventional optics sights than those found in ordinary T-72B3s. This tank's gunner would act as the marksman for the longest-range engagements, while its commander could act as a spotter for the rest of the company
With a T-90A company, you might have a T-90M as a command tank, and also replacing another tank in the company. And then everything else would be the same as above.
As you can see the idea mimics the idea of specialization within an infantry squad. Machine-gunner, marksman, RPG team, etc...
Within an infantry squad, it's rather easier to co-ordinate and specialize in this way than within a tank company; where everything has to be done through radio commands and orders passed down through commanders down to crews.
However this is where the latest generation of battlefield management systems come in, including the sort of systems that are being introduced in the latest gen tanks.
What do you think people?
Feasible? Has been tried already? Or would the logistics complications rule it out as not worth it?
One smart thing the Germans did at the battle, was not to group their Tigers up into their own formations, but spread them around all the existing tank formations. What you ended up with was tank companies and groups consisting of multiple different types of tanks, including the Tigers. The Tigers would spearhead each assault and moving column, and would essentially act as shields for the tanks behind them.
This mitigated the effect and tactics of Soviet AT artillery very significantly. The Soviet 76mm AT guns could only reliably penetrate a Tiger frontally from about 300m. Thus upon sighting the presence of Tigers in an advancing formation, they could not open fire at 1-2km, but had to wait until the tanks were nearly on top of them - even if the majority of the German force otherwise consisted of Panzer IIIs and IVs. If the AT grouping were successful in concealment until then, they would usually knock out some tanks, but the position would ultimately be overrun.
It was a similar story for the T-34s entrenched in defensive positions.
The Soviet 45mm guns meanwhile, which made up more of the Soviet AT force than anything else - were not very effective against even German medium tanks on a good day, and stood no chance against Panthers and Tigers. Thus they were discouraged from engaging at all, and could only rely on ambush tactics.
The end result is that barely any Soviet AT guns had survived to the end of the German offensive, and the start of the Soviet attempted counterattack.
Anyway this got me all thinking
What would be the feasibility of mixing up tank companies today and creating specializations within them, so that there is a counter to any tactic the enemy wants to adopt?
AFAIK nothing like this concept is employed in either the Russian tank force or the NATO formations today.
Taking for example a T-72B3 company.
The command tank could be equipped with an APS and the very latest reactive armour. Possibly along with it another tank could be equipped the same way as well. This would not only afford more protection to the most crucial tank in the formation, but would discourage the enemy from engaging at all, if they knew that what they had was unable to penetrate the lead tank's protection.
Taking the concept further, another T-72B3 of the company, could instead be swapped out for a BMPT-72, and would be used to suppress AT positions, infantry in dug-outs, bunkers or buildings.
Another tank could be fitted with a bias towards tank-launched missiles as opposed to normal rounds, and fitted with more sophisticated thermal and conventional optics sights than those found in ordinary T-72B3s. This tank's gunner would act as the marksman for the longest-range engagements, while its commander could act as a spotter for the rest of the company
With a T-90A company, you might have a T-90M as a command tank, and also replacing another tank in the company. And then everything else would be the same as above.
As you can see the idea mimics the idea of specialization within an infantry squad. Machine-gunner, marksman, RPG team, etc...
Within an infantry squad, it's rather easier to co-ordinate and specialize in this way than within a tank company; where everything has to be done through radio commands and orders passed down through commanders down to crews.
However this is where the latest generation of battlefield management systems come in, including the sort of systems that are being introduced in the latest gen tanks.
What do you think people?
Feasible? Has been tried already? Or would the logistics complications rule it out as not worth it?

Mir- Posts : 4122
Points : 4120
Join date : 2021-06-10
Yes those Russian anti-tank guns were not the best. The Germans had equally terrible anti-tank guns at the beginning but ended up with superb guns towards the latter half of the war.
Anyway with regard to your question I would stick to the same type of tank in the same company and perhaps fit a single company with more powerful tanks like the T-90M's or Armata for the breakthrough fist.
Say you have a company of T-90A's with a T-90M as the command element it will probably put a huge target on the T-90M and it may get disabled very quickly on the battlefield?
Anyway with regard to your question I would stick to the same type of tank in the same company and perhaps fit a single company with more powerful tanks like the T-90M's or Armata for the breakthrough fist.
Say you have a company of T-90A's with a T-90M as the command element it will probably put a huge target on the T-90M and it may get disabled very quickly on the battlefield?


 LMFS
LMFS